Back in 2005, when Peter Rodgers, the architect of NetKernel and Father of Resource-Oriented Computing, was presenting at the Web Services Edge Conference, he is credited to have first introduced the term ‘Micro Web Services’, while making a point for REST services and putting forth the idea of ‘Software as Micro-Web-Services’. With a background of doing intensive work in Hewlett Packard Lab’s Dexter Research Project, Peter Rodgers has been actively involved in researching how large-scale complex software can be made robust to change and making the code less brittle in nature, with a key focus on resource-oriented computing.
And this is likely to be where the story of microservices or microservices architecture started.
Microservices.io defines microservices as an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of services that are highly maintainable & testable, loosely coupled, independently deployable, organized around business capabilities, and owned by a small team. With microservices, one can carry out rapid, frequent, and reliable delivery of complex, large-scale software. Microservices also empowers an organization to evolve its technology stack.
The essence of microservices is that monolithic statues can be historical landmarks, but monolithic applications can’t. Monstrous monolithic applications can be extremely hard and super slow to manage, change, grow, and update.
Simply put, “Microservices are an architectural approach to building applications”, says Red Hat. With microservices one team’s work will not break the entire app, and new components can be built for the app much faster to meet the changing business needs.
Why do we need microservices?
Microservices architecture breaks an app down to its core functions. This is also the primary reason that sets microservices apart from monolithic architecture. Each core function is regarded as a service and is built & deployed independently. So, even if one service is adversely impacted, the other services can still remain up & running, unaffected. This makes it a crucial part of the technology-side of DevOps, while making the implementation of a CI/CD pipeline more seamless. Microservices enable faster development across multiple environments, which is why they are critical to cloud-native application delivery.
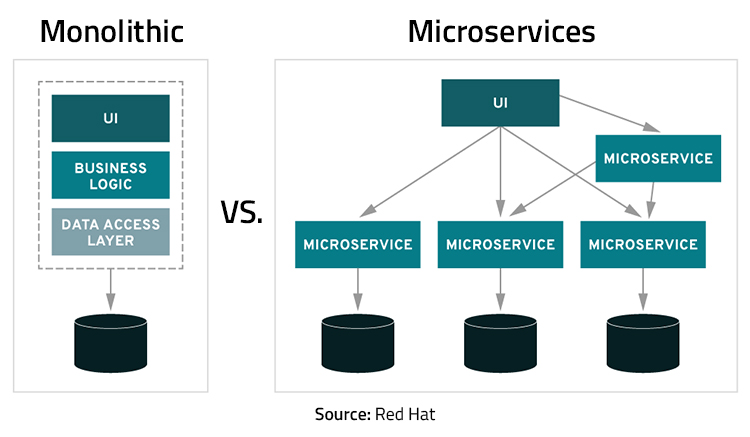
Monolithic vs. Microservices Architecture
Here’s a quick comparison between monolithic architecture and microservices architecture:
It’s the holiday season, so let us explain this with a festive example. Suppose you go to your favorite bakery to buy some of your favorite plum cake. Unfortunately, the supplier who used to provide this bakery with an indispensable ingredient for the plum cake has had an incident at his end due to which he has been unable to supply the ingredient to the bakery. Now, the bakery has been working to arrange an alternate supplier, but it does throw the costing, pricing, and production plans of the plum cake to chaos for the time-being till the solution can be found. However, the bakery still has other holiday-special products available – hot chocolate bombs, gingerbread cookies, yule logs, coffee cakes, etc. because they have diversified their supplier base. So, the bakery is still up and running, while it is working to find a solution of how to begin plum cake production as soon as possible. Once the supply issue is sorted, plum cakes will be up on the shelves. But their absence does not affect the overall functioning of the bakery, except affecting a certain aspect or function of it. It would leave the customers a little disappointed, but while the other fare is still available, chances are the customer experience wouldn’t be all that negative either. This is possible because the bakery did not depend on a single supplier for everything and has divided itself into separate services. Due to this, breakdown in one service does not affect the overall functioning of all the other services. Also, a new service can be added without affecting the overall functioning of the application, or the bakery in this case. This is the entire logic behind containers and microservices.
Did this sound like something familiar?
Of course it did!
Because microservices architecture is quite similar to service-oriented architecture or SOA which is a well-established way of designing software.
Microservices vs. Service-Oriented Architecture
Service-oriented architecture structures the application into discrete, re-usable services. The services are organized based on specific business processes and need to follow a fixed communication protocol, such as SOAP, ActiveMQ, or maybe Apache Thrift. These services can communicate with each other through an Enterprise Service Bus (ESB). Together, these services then form an application, integrated using the ESB.
The SOA does overcome the major limitation of monolithic architecture, but it creates a new bigger limitation – the ESB. If the ESB fails, the whole application still fails. So, instead of offering a host of opportunities, the SOA holds the potential to become quite a major bottleneck for the enterprise, thanks to the Enterprise Service Bus.
This does not happen when you use the microservices architecture. With microservices, the communication between the services happens almost statelessly. This results in applications being more fault-tolerant, and it overcomes the limitation of the ESB.
So, in a way it could be said that microservices is not such a new concept, considering a form of it was already present in the service-oriented architecture. With the advancement in containerization technologies, microservices architecture became even more viable and popular.
What are the benefits of using microservices architecture?
Here are some of the top benefits of using microservices architecture for developing applications:
- Shorter time-to-market: Microservices enables shorter development cycles, supporting more agile development, and faster rollout of updates
- Better scalability: With growing demand, microservices can step up, and enable deployment across multiple servers and multiple infrastructures.
- Better resilience: When used effectively, the independent services in the architecture do not affect one another. So, if one service fails, the whole application will still stand strong. This wouldn’t be the case if you use monolithic architecture.
- Ease of deployment: Apps built using microservices architecture are modular and smaller. Provided you have a proper service mesh layer in place, coordinating between different components and layers wouldn’t be a problem at all. And the deployment will go as smooth as butter.
- Better accessibility for developers: With microservices, the application is not one monstrous mess, but a mix of smarter, smaller, easy to understand pieces. This makes it much easier for developers to access, update, and work on the different pieces of the application. This also makes processes more efficient and quicker. And when you are using an agile development model, nothing helps more than quicker, more efficient processes.
- More freedom: Microservices architectures use Polyglot APIs. This in turn gives developers the freedom to choose the best language and technology for the functions at hand. More freedom to developers results in a better final product.
How can you learn microservices architecture?
If you are looking for the best microservices training, you have come to the right place.
Cognixia – the world’s leading digital talent transformation company offers the best-in-class Spring Boot and Microservices Boot Camp that can help you learn how to build fault-tolerant, resilient, cloud-native applications using Spring Boot and microservices architecture. This microservices training is an intensive hands-on boot camp delivered by some of the best most experienced microservices trainers in the world. This is perfect course to get certified in microservices and Spring Boot, as it covers:
- Developing enterprise applications using microservices architecture
- Building and deploying cloud-based, scalable, and fault-tolerant applications
- Containerizing applications using Docker
- Deploying Spring Boot applications to AWS cloud
If you wish to advance your career in microservices, enrolling for the best microservices training and getting certified is the way to go. With this microservices certification course, you also get lifetime access to all the learning material and video sessions via our LMS. At the end of the course, you get an internationally recognized Microservices Certificate from Cognixia.
So, what are you waiting for? Visit here to know more now!
~ Sunny Shah
